Topology?
Topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of devices connected in a network.
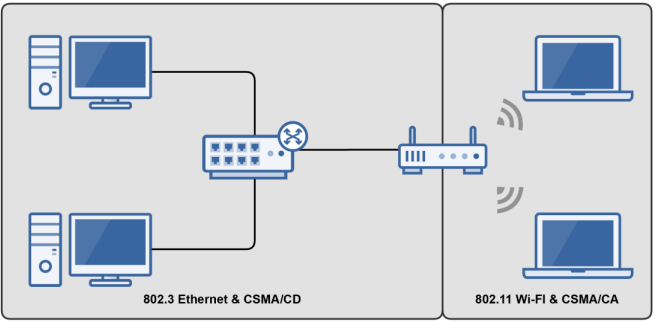
Physical topology: It refers to the actual layout of buildings and the physical placement of devices.
→ This includes where servers, switches, firewalls, and printers are physically located.
Logical topology: It refers to the way data flows through the network
Wired Topologies:
Bus Topology: All devices are connected to a single coaxial cable
→ If one device fails, it can potentially bring down the entire network.
Ring Topology: All devices are connected in a circular manner.
→ Data travels in one direction, and if the network is interrupted, data transmission fails.
Star Topology: All devices are connected to a central switch.
→ This is the topology most commonly used in modern networks. If the central switch fails, it needs to be replaced.
Mesh Topology: Every device in the network is connected to every other device.
→ Installation costs are high, so important devices are often designed using a partial mesh topology.
→ Data can be transmitted through multiple paths.
Wireless Topologies:
Ad hoc Topology: There is no central connecting device, and devices are connected in a peer-to-peer manner.
Infrastructure Topology: A wireless network topology where there is a central connecting device.
Mesh Topology: One network device is connected via wired connection,
while the other network devices are connected wirelessly.
→ This creates a strong wireless network.

I discovered that it's possible to create a hybrid topology by combining star topology and partial mesh topology
using the Cisco Packet Tracer program.
'Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Network_OSI Layer 2 (3) | 2024.09.09 |
|---|---|
| Network_Packet Structure (3) | 2024.09.03 |
| Network_Overview of network devices (2) | 2024.08.27 |
| Network_How to Network Systems work? (0) | 2024.08.08 |
| Network_Basic Concepts (2) | 2024.08.05 |


